Venous malformations are one of several types of vascular malformation, which are abnormal clusters of blood vessels. Venous malformations specifically involve the veins, which are responsible for carrying blood back to the heart. Understanding these malformations is crucial for managing their symptoms and improving patients’ quality of life.
Characteristics of Venous Malformations
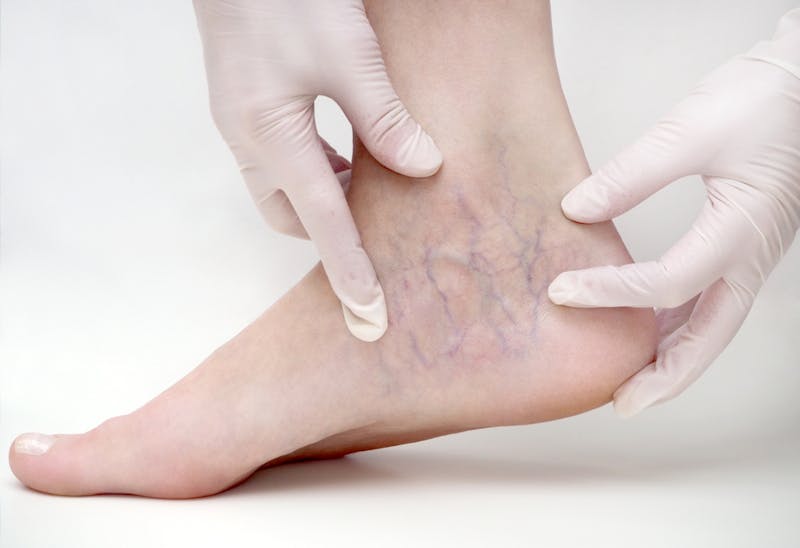
Venous malformations are the most common vascular malformations, characterized by abnormally dilated veins. They can occur anywhere in the body but are often found in the skin, mucous membranes, and soft tissues. These vascular lesions may present as a blue or purplish hue on the skin, often described as a port wine stain. The malformations can vary greatly in size, ranging from small patches to larger lesions that involve extensive areas of the body, like the neck regions or extremities.
The Causes and Risk Factors of Venous Malformations
These vascular anomalies are usually congenital, meaning they are present at birth. The precise cause of venous malformations is not fully understood, but they are believed to result from errors during the developmental stage where vascular channels form. Risk factors include family history and genetic predispositions. Unlike arteriovenous malformations, which create abnormal connections between blood from arteries to veins, venous malformations are comprised solely of venous blood vessels.
Genetic Factors and Congenital Development of Venous Malformations
Research has found that some venous malformations are associated with mutations in the TIE2 gene, providing insight into the chemical structure of these blood vessel malformations. These aberrant genes affect the way blood vessels grow, leading to venous anomalies that become apparent early in life. Congenitally, venous malformations are often present but may not be visible until later in adult patients as they enlarge over time with hydrostatic blood pressure.
Identifying Symptoms and Signs of Venous Malformations
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the location and size of the malformation. Common signs include:
- Visibly dilated veins or bluish marks on the skin (port wine stain)
- Swelling or a lump in soft tissues, especially when standing or crying
- Discomfort or pain in the affected area
- Functional limitations, if the malformation compresses adjacent structures
Some patients may report a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to significant pain or complications such as bleeding from superficial lesions or chronic pain syndrome.
Diagnosis of Venous Malformations
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical evaluation by a health care provider, possibly Dr. Panossian, followed by imaging studies to ascertain the extent of the malformation. Common diagnostic tools include ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and sometimes angiography. Imaging helps differentiate venous malformations from other types, such as lymphatic malformation or cavernous malformations, and they can show detailed features like the depth of deep lesions and the involvement of adjacent structures like the facial nerve or spinal cord.
Treatment Options for Venous Malformations
Interventional Radiology Procedures
- Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a solution directly into the malformed veins to cause them to collapse. Procedures like absolute ethanol sclerotherapy or closure by foam sclerotherapy reduce the size of the malformation and associated symptoms.
- Embolization: This technique is used to block abnormal veins, preventing blood drainage through them.
Surgical Approaches to Treatment
- Partial Excision: Surgery may involve removing a part of the venous malformation if the malformation is causing significant problems or is aesthetically undesirable. It’s critical to balance the removal of affected tissue with the preservation of normal tissue and important structures like nerves.
- Complete Excision: In some cases—for instance, if there is recurrent bleeding or pain—complete excision might be recommended. However, this is more challenging in cases where malformations infiltrate into normal tissues or critical areas like brain tissue or bone structures.
In a treatment plan, multiple approaches may be considered, reflecting a single treatment approach or multidisciplinary treatments depending on the individual’s needs, aligned with established treatment guidelines.
Managing Complications Associated with Venous Malformations
Venous malformations can lead to various complications over time, such as blood clots, tissue necrosis, or even a potentially life-threatening pulmonary embolism. A tailored care plan might include:
- Compression Garments: Compression stockings can alleviate symptoms by providing consistent pressure to the area, which helps control swelling and pain.
- Medication: Anticoagulants could be prescribed to manage blood clots, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up is necessary to watch for the development of new symptoms or complications, such as facial paralysis or changes in the angular vein.
Prompt treatment of complications not only improves symptoms but also contributes to a better quality of life, reducing the risk of severe outcomes like brain damage.
Long-Term Management and Monitoring of Venous Malformations
Follow-up Care and Ongoing Treatment Strategies
A treatment strategy’s effectiveness needs to be continuously evaluated. Follow-up care often involves:
- Regular visits with a health care provider, possibly with Dr. Panossian, to monitor growth and symptoms.
- Re-evaluation of treatment options, as malformations may change over time.
- Consistent use of add-on therapy, such as compression garments, to aid treatment efficacy.
Patients with venous malformations, specifically those with complicated lesions or extensive lesions, often require lifelong management. This ensures that new challenges to patient health, such as changes in lesion size or the development of residual lesions, are addressed promptly and effectively.
Impact on Quality of Life and Psychological Well-being
The physical presence of venous anomalies can undoubtedly affect an individual’s quality of life. Visible lesions, such as those in the neck venous region or a port wine stain on the face, may lead to psychological distress and social stigma. Consequently, it’s essential for the care team to offer emotional support and appropriate resources, encouraging patients to maintain an active life despite their condition. Some individuals may benefit from counseling or support groups as part of their care plan.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Visit: Questions and Considerations
When visiting your healthcare provider for the management of venous malformations, consider the following:
- Medical History: Detail any past treatment, including laser treatments, surgical treatment, or previous complications like blood clots.
- Symptoms: Discuss any new or worsening symptoms, such as increased pain or changes to existing malformations.
- Questions: Prepare a list of questions related to potential treatment options, including sclerotherapy, surgical options, and multidisciplinary team management.
- Expectations: Talk about your goals and what you hope to achieve, whether it’s pain relief, improvement in appearance, or the prevention of further complications.
By being proactive and well-prepared for appointments with a doctor like Dr. Panossian, patients can ensure that they’re actively participating in the management of their condition.
Venous malformations present unique and often complex challenges. While the condition can lead to significant functional limitations and emotional distress, modern approaches to treatment and management offer hope.
From minimally invasive procedures like sclerotherapy to carefully planned surgical interventions, treatment options are tailored to individual needs. The aim is to minimize symptoms, prevent complications, and ultimately enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Living with venous malformations is a journey that can be fraught with uncertainty, but with the right support and a robust treatment plan, patients can navigate their condition and lead fulfilling lives.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Panossian today to discuss your individual needs and begin a comprehensive approach to treatment that aims to enhance your quality of life.


