Dr. Andre Panossian in Pasadena provides effective management of neurofibromatosis symptoms, improving the quality of life for those affected for more than a decade.
With the right treatment strategies, it is possible to manage the symptoms effectively.
Understanding Neurofibromatosis and Its Impact on Daily Life
Neurofibromatosis, a genetic disorder, significantly impacts daily life due to its diverse clinical manifestations.
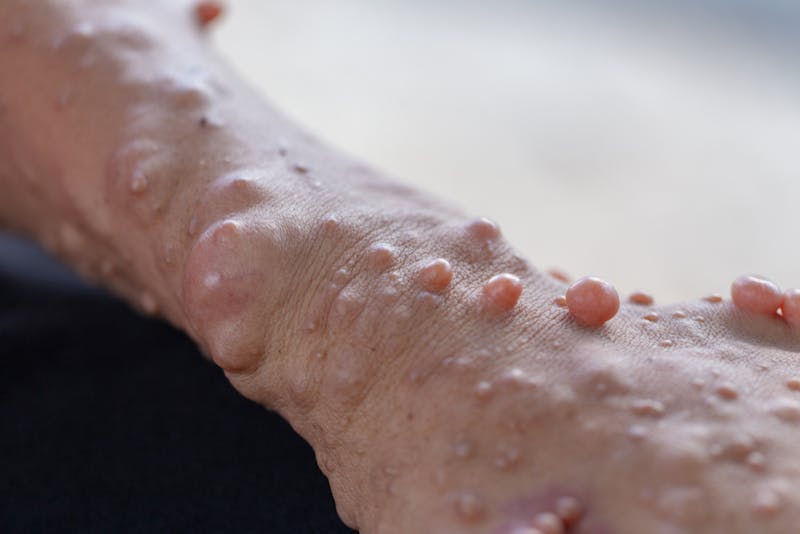
The most common type, Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), often presents with café-au-lait spots, subcutaneous neurofibromas, and sphenoid wing dysplasia. These symptoms can lead to physical discomfort, cognitive impairment, and visual acuity issues, affecting the quality of life of patients with neurofibromatosis.
Also, complications such as renal artery stenosis and congenital heart disease may arise. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are essential for managing this genetic condition effectively.
Common Symptoms and Their Effect on Well-Being
Patients with neurofibromatosis types 1 and 2 may experience the following symptoms:
- Café-au-lait spots, subcutaneous neurofibromas, and plexiform neurofibromas along nerves affect self-esteem, cause physical discomfort or pain, and cause functional problems depending on their location.
- Skeletal manifestations, including bone dysplasia and sphenoid wing dysplasia, affect visual acuity and cause physical discomfort.
- Internal neurofibromas and peripheral nerve sheath tumors may increase the risk of malignant transformations and additional health risks like renal artery stenosis.
Symptoms vary greatly between individuals, underlining the importance of personalized care in managing this genetic disease and its complex clinical manifestations.
Types of Neurofibromatosis
Type 1
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), a dominant disorder, manifests with internal neurofibromas, sphenoid wing dysplasia, and a risk of malignant tumors. NF1 is the most common type of neurofibromatosis. Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 often experience skin changes, such as café-au-lait spots and bone deformities, impacting their visual acuity. The natural history of NF1 varies, necessitating personalized treatment for people with neurofibromatosis type 1.
Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
In pediatric patients, neurofibromatosis type 1 can manifest in several ways. Children with neurofibromatosis type 1 may develop optic glioma, also known as optic pathway glioma or optic nerve glioma, which can affect their vision. Skeletal manifestations are also common, and these children may face a heightened risk for myelomonocytic leukemia.
Adults with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Adults with NF1 face risks like atypical neurofibromas, peripheral nerve sheath tumors, and an increased risk of breast cancer. Advanced age in adults influences symptom progression and life expectancy. The care of adults in NF1 involves regular monitoring for tumor growth and bone dysplasia.
Type 2
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) is characterized by nerve tumors, particularly vestibular schwannomas, leading to hearing and balance issues in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 2. Additional risks include spinal tumors and visual impairments, necessitating regular neurological and ophthalmological evaluations.
Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Children with NF2 require early intervention for hearing and vision challenges. Regular monitoring for vestibular schwannomas and other neurological manifestations is essential to address the special healthcare needs of children with neurofibromatosis type 2.
Adults with Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Adults with NF2 need comprehensive care focusing on chronic symptoms and tumor management, including spinal tumors. Supportive technologies for hearing loss and regular check-ups for neurological changes are crucial for the care of adults with neurofibromatosis type 2.
Schwannomatosis
Schwannomatosis is a type of neurofibromatosis that is less common than neurofibromatosis type 1 and neurofibromatosis type 2. This condition is characterized by the development of benign tumors, known as schwannomas, on peripheral nerves throughout the body.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Neurofibromatosis
The treatment of neurofibromatosis aims to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and address aesthetic concerns.
Medications Used in Neurofibromatosis Management
Medication is crucial for symptom management, primarily for pain relief. It can also help control tumor growth, sometimes in combination with radiation therapy.
Surgical Interventions and When They’re Necessary
Surgical interventions are vital for managing neurofibromatosis, particularly in complex cases like plexiform neurofibromas and peripheral nerve sheath tumors.
Surgical excision is often used to treat these tumors in patients, especially if they cause chronic pain, show rapid growth, or are on peripheral nerves.
Managing Cutaneous Symptoms: Care for Neurofibromas and Skin Conditions
In neurofibromatosis, cutaneous symptoms like neurofibromas and café-au-lait spots are common.
Dermatological Treatments and Skin Care Tips
To manage neurofibromatosis-related skin conditions, treatments such as laser therapy can lessen the visibility of café-au-lait spots. Topical creams and ointments provide relief from skin discomfort. Routine skin care with gentle cleansers and moisturizers maintains skin health, while sun protection is crucial to prevent symptom aggravation.
Navigating the Challenges of Plexiform Neurofibromas
Plexiform neurofibromas (complex benign tumors) can significantly impact comfort and function.
Pain Management Strategies
Chronic pain is a common problem for those with plexiform neurofibromas. Management options include medications like gabapentin and pregabalin for nerve pain.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Options
Surgical excision is often used to treat these tumors in patients, especially if they cause chronic pain, show rapid growth, or are on peripheral nerves.
Non-surgical methods like radiation therapy are alternative options to reduce tumor size and ease symptoms. However, it’s important to note that radiation therapy also comes with its own set of risks and side effects, and these should be discussed thoroughly with the healthcare provider.
Addressing Hearing and Vision Problems in Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis can lead to sensory challenges that are particularly common in individuals with Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) but can also occur in those with other types of the condition.
Regular Screenings for Early Detection
Frequent screenings for hearing and vision are essential. These allow for the early identification of changes and risk factors, which enables prompt and effective intervention. Regular appointments with audiologists and ophthalmologists are recommended for those with neurofibromatosis.
Supportive Technologies and Treatments
To manage hearing and vision issues, various supportive technologies and treatments are available. Hearing loss may be addressed with devices like cochlear implants or auditory brainstem implants. Vision impairments can be managed with corrective lenses or surgical interventions tailored to the individual’s needs.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Enhancing Mobility
Physical therapy can be pivotal in symptom management for neurofibromatosis. It helps improve muscle strength, coordination, and flexibility, which are often compromised by tumor growth on nerves. Physical therapy also offers pain relief and can lift the patient’s mood.
Individualized Exercise Plans
Tailored exercise plans are designed to meet the unique needs and capacities of individuals with neurofibromatosis. These plans typically blend stretching, strengthening, and aerobic exercises. Regular engagement in such physical activities is beneficial for enhancing overall health and well-being.
Psychological Support for Individuals and Families Affected by Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis, a genetic disorder, poses emotional challenges due to its unpredictability, chronic pain, and potential for social isolation. This includes strategies for managing stress, anxiety, and depression, which are particularly important for pediatric patients and those with a family history of the condition.
Counseling and Therapy Options
Individual therapy, family therapy, and support groups provide a supportive environment for individuals and families, including those dealing with cutaneous neurofibromas or optic pathway gliomas, to express emotions and learn coping strategies.
It is recommended that patients seek help from mental health professionals familiar with genetic conditions and the unique challenges of neurofibromatosis.
Nutritional Considerations and Diet in Managing Neurofibromatosis Symptoms
A nutritious diet can support overall health and help manage the symptoms of neurofibromatosis. Nutritional needs can vary based on individual circumstances, so it’s advisable to meet with a registered dietitian to determine the proper diet.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial in managing neurofibromatosis. This allows for early detection of new symptoms or changes in existing ones and timely intervention. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, including neurologists, dermatologists, audiologists, and ophthalmologists, are recommended.
Educating Patients and Families about Neurofibromatosis
Education plays a pivotal role in managing neurofibromatosis. It is essential for patients and their families to have a comprehensive understanding of this complex medical condition, its potential impact on daily life, and the various treatment options available.
Discover the latest advancements in neurofibromatosis treatment and management with Dr. Panossian in Pasadena, CA. As emerging studies unveil potential complications and symptoms like café-au-lait spots and bone deformities, it’s crucial to consult an expert. Schedule your consultation with Dr. Panossian today for personalized care and cutting-edge insights.


